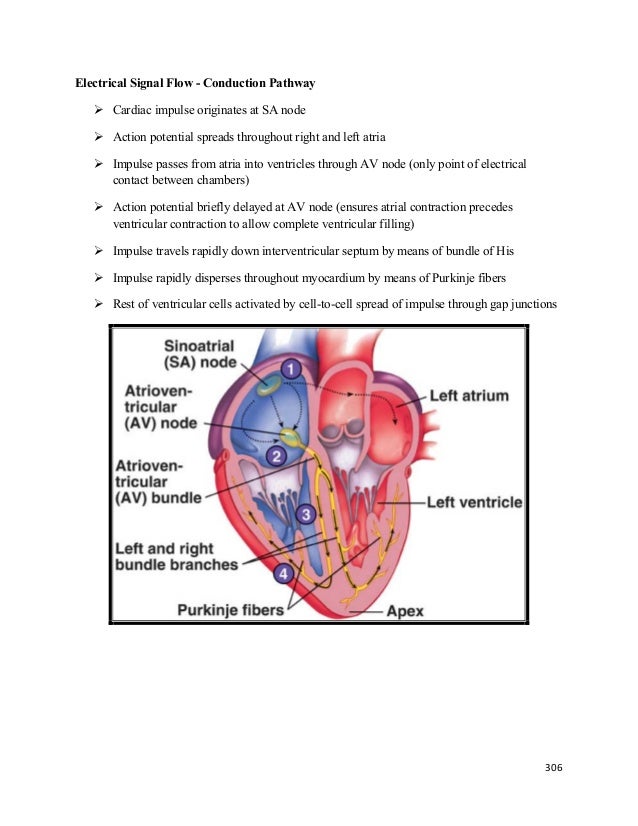
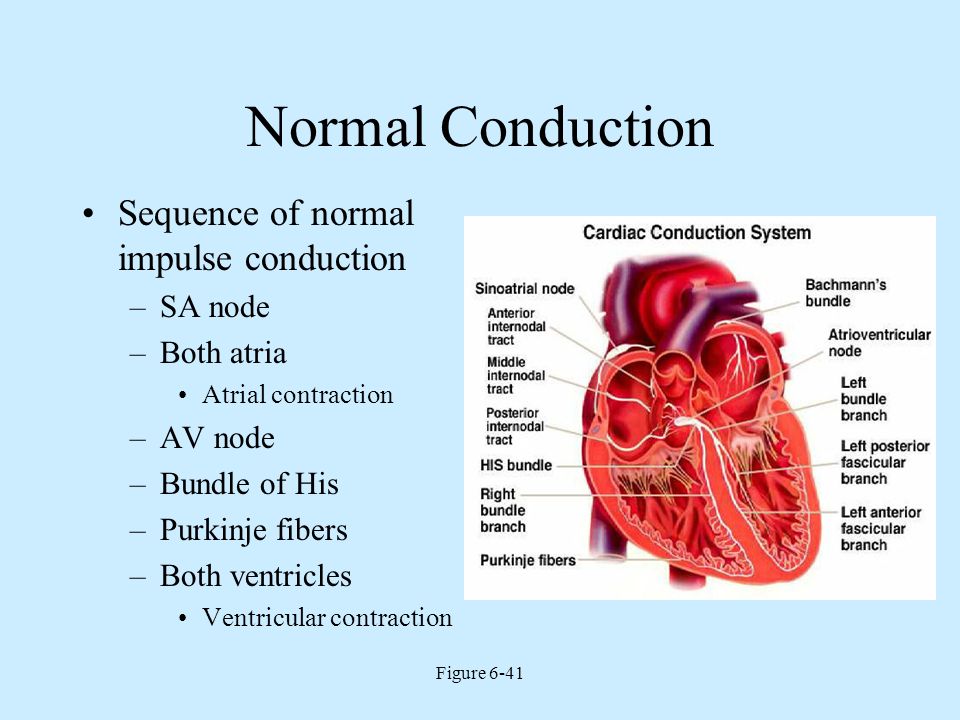
Answers initiates the heartbeat through cells that can depolarize on their own allows both atria to contract rapidly in response to a signal from one node has unique muscle fibers that canThe _____ is the largest vein that drains the heart the coronary sinus movement of blood from the left ventricle through the body is called systemic circulation the thick, muscular middle layer of the heart wall that contains the atrial and ventricularImpulse that propagates through the atria to the atrioventricular node, where a delay permits ventricular filling before the electrical impulse proceeds through the specialized HisPurkinje conduction system that spreads the electrical signal at speeds of meters per second throughout the ventricles This electrical impulse propagates diffusively
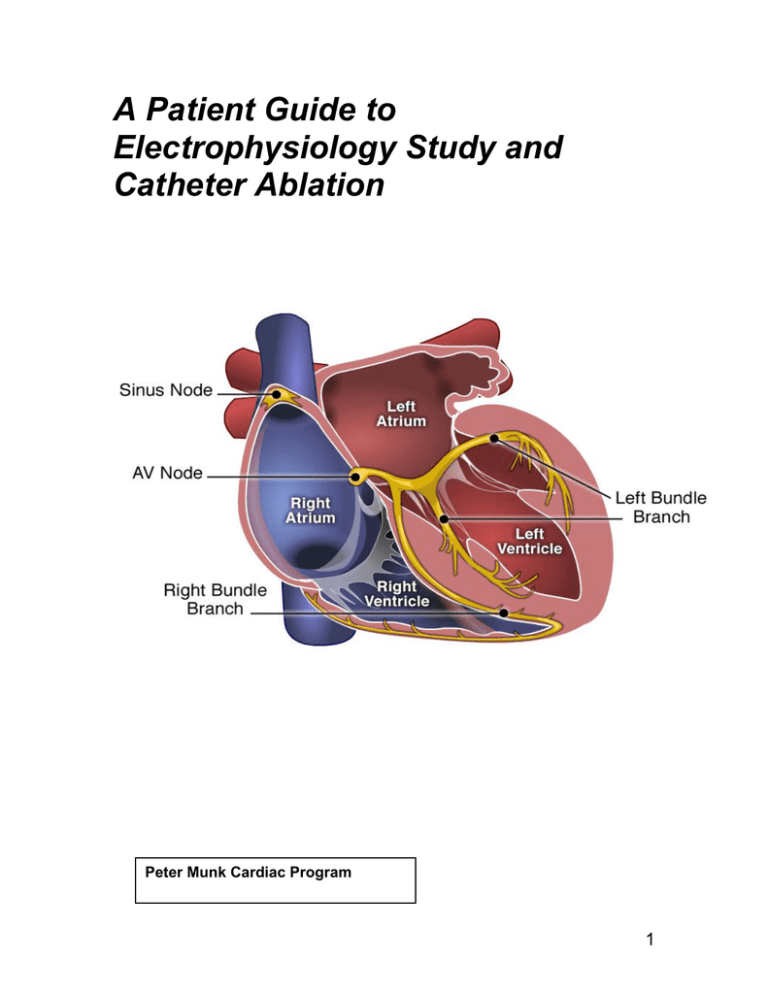
Electrophysiology Study And Catheter Ablation
To gather information about impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricle study the
To gather information about impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricle study the-The thinwalled atria receive blood returning to the heart and pump blood into the ventricles The thickerwalled ventricles pump blood out of the heart The left ventricle is thicker than the right ventricle because the left side of the heart has a greater workload The entrance and exit of each ventricle are proConduction system • This pause allows for the blood in the atria to move into the ventricles before the ventical contract • Impulses continue into the ventricle through the bundle of His which contain both right and left bundle branches • These impulses produce an electrical current which can be picked up by electrodes attached antibody




The Cardiac Cycle Biology For Majors Ii
Electrophysiologic Study 1 Electrophysiologic Study Pacing Methods & EP Testing1 2 Pacing Methods Programmed Electrical Stimulation (PES) PES is a pacing technique using an intermittent or continuous introduction of an electrical current to the intracardiac surface through an electrode catheter Cells near the electrodes depolarize and begin a wave of depolarization WolffParkinsonWhite syndrome is a form of anomalous AV conduction or ventricular preexcitation Ventricular preexcitation is said to exist when conduction of a supraventricular impulses occurs via an accessory pathway which bypasses the AV node Conduction through the accessory pathway allows premature activation of the ventricularThe atrial conductive system is organized so that the cardiac impulse does not travel from the atria into the ventricles too rapidly;
Conduction is how electrical impulses travel through your heart, which causes it to beat Some conduction disorders can cause arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats Three common conduction disorders are Bundle branch block Explaining the problem Normally, electrical impulses travel down the right and left branches of the ventricles at the same Using an appropriate (and impressive) array of experimental techniques, the authors demonstrate that the crocodilian heart has a specialized atrioventricular bundle that provides for electrical signals to be conducted from the atria to ventricle in a timely fashion, insuring the necessary delay required for blood to be transmitted between these chambersThe fibers of cardiac muscle are interconnected by special junctions that provide for the conduction of impulses across the entire myocardium which allows the heart to contract as a single unit Heart chambers The heart is composed of four chambers The two smaller, superior chambers called the atria The two larger, inferior chambers called the
Study free flashcards and improve your grades period in the cadiac cycle when blood enters the relaxed ventricles from the atria Bottom number of a blood pressure reading neurological tissue in the center of the heart that receives and amplifies the conduction of impulses from the sinoatrial SA node to the bundle of his (router)Slows conduction o fthe impulse as it travels fromteh atria to the ventricles, PROVIDING A DELAY between activation and contraction of f the upper and lower heart chmbers (this allows atria to contract fist then vent) the muscle impulse travels fromt eh Av node tot he _____ atrioventricular bundle (bundle of his) describe bundle of his?When an electrical impulse reaches the AV node, it is slowed for a brief period of time so that A blood can pass from the artria to the ventricles B the SA node can reset and generate another impulse C the impulse can spread through the Purkinje fibers D blood returning from the body can fill the atria




A P 2 Unit 2 Study Guide Flashcards Quizlet
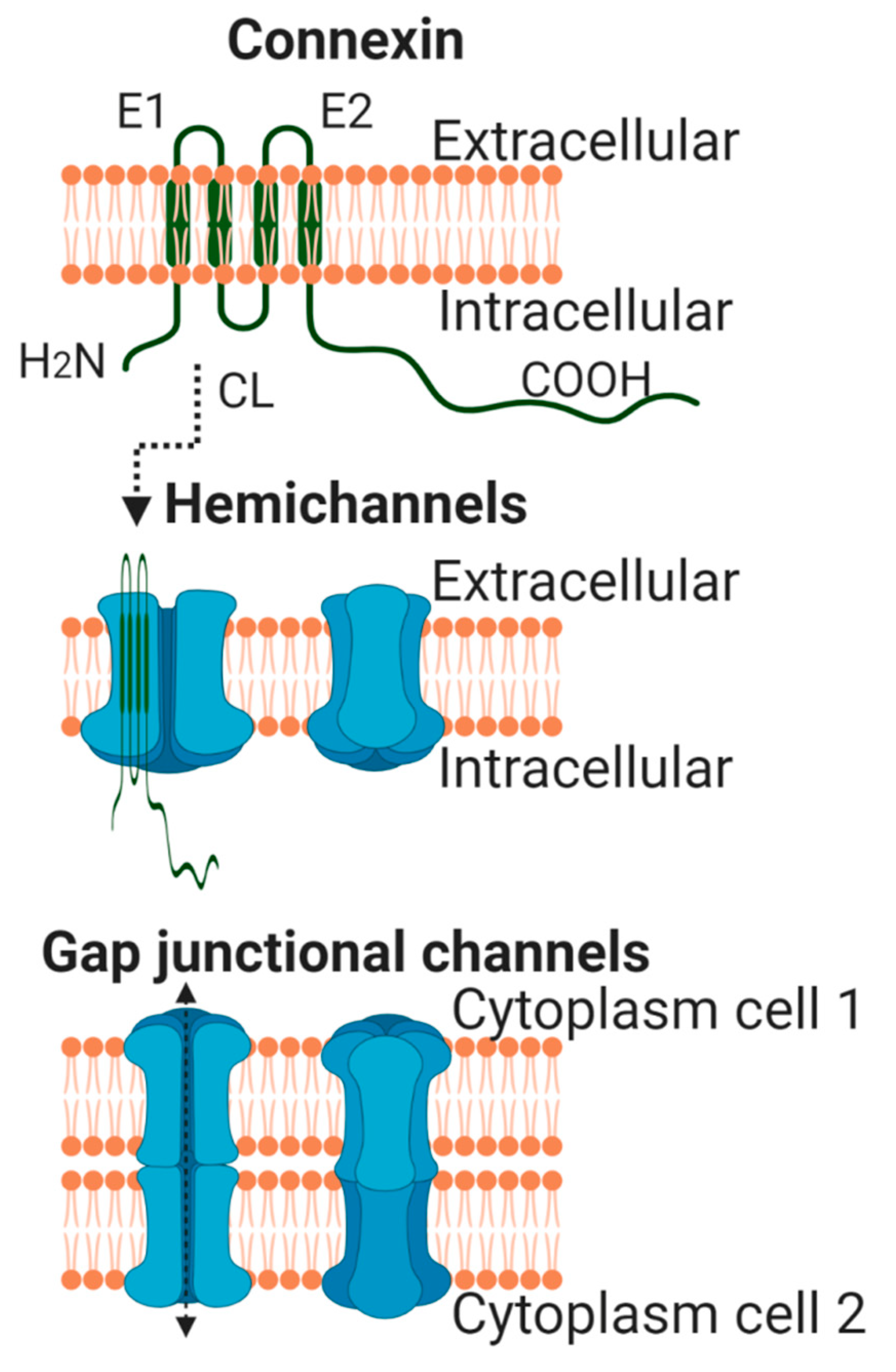



Ijms Free Full Text Connexins In The Heart Regulation Function And Involvement In Cardiac Disease Html
This impulse spreads from its initiation in the SA node throughout the atria through specialized internodal pathways, to the atrial myocardial contractile cells and the atrioventricular node The internodal pathways consist of three bands (anterior, middle, and posterior) that lead directly from the SA node to the next node in the conductionFluid accumulated in tissues as blood backs up – in lungs if left ventricle is most affected, in systemic vessels if right ventricle is most affected 5 Arrhthmias (dysrhythmias) – abnormality or irregularity of heart rhythm they result from a disturbance in the conduction system, either in the generation of impulses or their conductionThe apex (tip of left ventricle) is where the heart is heard the best (under left breast) Normal heart sounds heard with a stethoscope are produced by the closing of the heart valves The first sound is S1 and is heard at the beginning of systole as "lubb" when the tricuspid and mitral valves close The second heart sound is S2 and is heard at the start of diastole as "dupp" when the
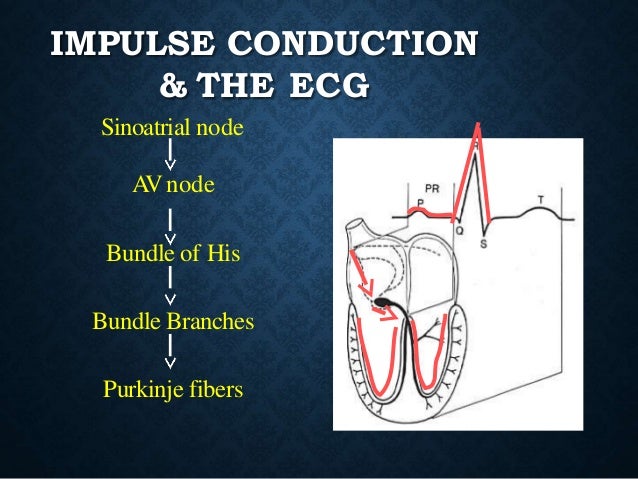



Basics Of Ecg



Modeling An Excitable Biosynthetic Tissue With Inherent Variability For Paired Computational Experimental Studies
Following this step, the ventricles will then go into systole, which the atria will go into diastole Become a member and unlock all Study Answers Try it riskfree for 30 daysThis coordinates the contractions of the atria and ventricles so that the atria always contract before the ventricles, thus forcing blood from the atria to the ventricles The capacity automatically to generate propagated impulses is characteristic not only of the sinoatrial node, but of other elements of the conduction system as wellStart studying Interpreting a Rhythm Strip Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools
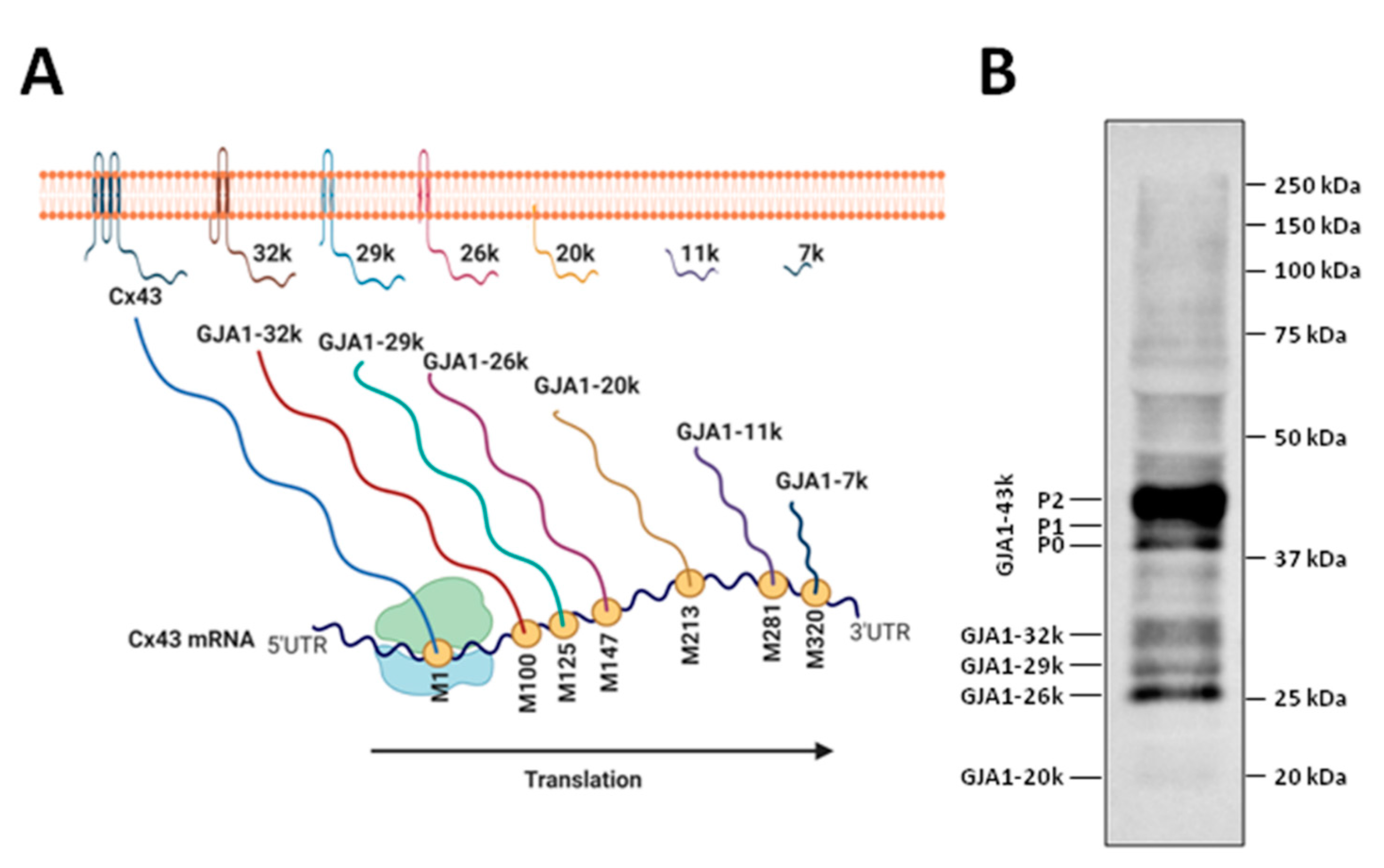



Ijms Free Full Text Connexins In The Heart Regulation Function And Involvement In Cardiac Disease Html



Modeling An Excitable Biosynthetic Tissue With Inherent Variability For Paired Computational Experimental Studies
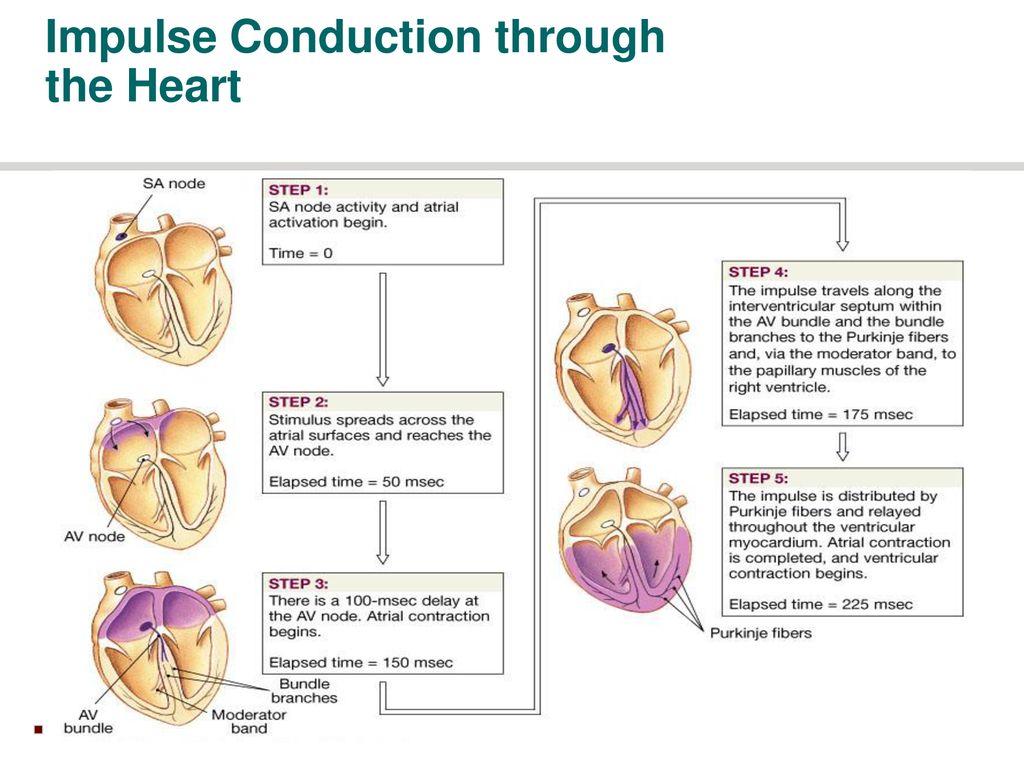
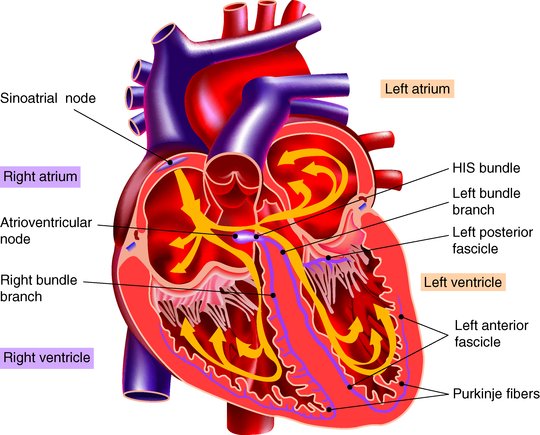
As electrical impulses from the SA node spread to cardiac muscle cells in the atria, those cells are stimulated to contract (atrial systole) The impulse moves from cells of the atria to a node of cells, called the atrioventricular (AV) node, located between the two ventricles The impulse is delayed momentarily by the AV nodeQuestion 25 Question The main property of the AV node is to Answer a forward % extra blood volume to the ventricles slow impulse conduction velocity/speed ensure a regular rhythm of impulse transmission promote atrial systoleThe signal travels down a bundle of conduction cells called the bundle of His, which divides the signal into two branches one branch goes to the left ventricle, another to the right ventricle These two main branches divide further into a system of conducting fibers that spreads the signal through your left and right ventricles, causing the




12 Hrs Ehra Ecas Expert Consensus Statement On Catheter And Surgical Ablation Of Atrial Fibrillation Recommendations For Patient Selection Procedural Techniques Patient Management And Follow Up Definitions Endpoints And Research Trial Design




Calameo 10 Mcu 18 Practical Cardiology 1st Edition
The impulse then reaches the atrioventricular node (AV node), which is the traffic cop of the heart and transmits the electrical impulse from the atriaThe order of impulse conduction in the heart, from beginning to end, is SA node, bundle branches, bundle of His, AV node, and Purkinje fibers SA node, bundle of His, AV node, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers Radiofrequency ablation revolutionized treatment of multiple cardiac arrhythmias The hottest current topic is ablative treatment of atrial fibrillation (AF) However, other supraventricular tachycardias (SVT) deserve attention This article describes mechanisms of SVT, psychological implications, concepts of ablation, and the role of ablation in treatment of SVT




Anisotropic Activation Spread In Heart Cell Monolayers Assessed By High Resolution Optical Mapping Circulation Research



Heart Block
Small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins responsible for initiating electrical conduction of the heartbeat, causing the atria to contract and firing conduction of impulses to the AV node neurological tissue in the center of the heart that receives and amplifies the conduction of the impulses from the SA node Background—The early phase of action potential (AP) repolarization is critical to impulse conduction in the heart because it provides current for charging electrically coupled cellsIn the present study we tested the impact of heart failureassociated electrical remodeling on AP propagation Methods and Results—Subepicardial, midmyocardial, and subendocardial Represents time taken for impulse to spread through the atria, AV node and bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers, to a point immediately preceding ventricular contraction 01 Disturbance in conduction usually in AV node, bundle of His, or bundle branches but can be in atria as well QRS Complex
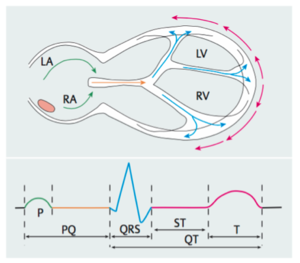



Electrocardiogram Ecg Cardiosecur




Atrial Flutter Surgical Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing Nursing Notes
Or reentry (disorder in impulse conduction), most are no life threatening, some associated with extremely fastView Notes Guided Reading #1 Cardiac Anatomy and Assessment from NUR 430 at Pennsylvania College Of Technology Kassie Smoyer 1/10/17 NUR 430 Adult Health Nursing II Guided Reading1) isovolumetric contraction 2) ventricular ejection 3) isovolumetric relaxation front 11 The depolarization of the SA node (from threshold to peak) is due to the inflow of ____ and _____ ions back 11 calcium and sodium front 12 The study of the heart and its disorders is known as




Anisotropic Activation Spread In Heart Cell Monolayers Assessed By High Resolution Optical Mapping Circulation Research




Cardiovascular Pathology The Perfect Preparation For Usmle Step 1 Heart Valve Heart
• The heart has 4 chambers right and left atria, right and left ventricle that are connect by valves • The atria are the two upper chambers separated by the interatrial septum into the left and right • Atria receive blood returning to the heart from the body • The muscles of the atria contract • Ventricles are the lower chambers Atrioventricular Valves AV valves between atria and ventricles Bicuspid (mitral) valve on the left Tricuspid valve on the right When valves are open blood drains from atria into ventricle When ventricle contract, valve flaps are forced shut, blocking blood from reentering 13Cardiac Conduction System The heart, a hollow muscular organ, is located in the center of the chest The heart has two sides, right and left The right and left sides of the heart each have To ensure that blood flows in only one direction, each ventricle has




Relationship Between Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation And A Novel Electrocardiographic Parameter P Wave Peak Time Sciencedirect




An Intelligent System For Pacemaker Reprogramming Sciencedirect
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs The atrium (an adjacent/upper heart chamber that is smaller than a ventricle) primes the pump In a fourchambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a doubleThe atria or ventricles Electrophysiologist A cardiologist who specialises in the electrical side of the heart, meaning the heart's rhythm Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) An abnormal heart rhythm Ventricles The two lower chambers of the heart The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs and the left ventricle pumps blood around the bodyThe atrioventricular conduction axis, located in the septal component of the atrioventricular junctions, is arguably the most complex structure in the heart It fulfils a multitude of functions




Answers To Revise As You Go
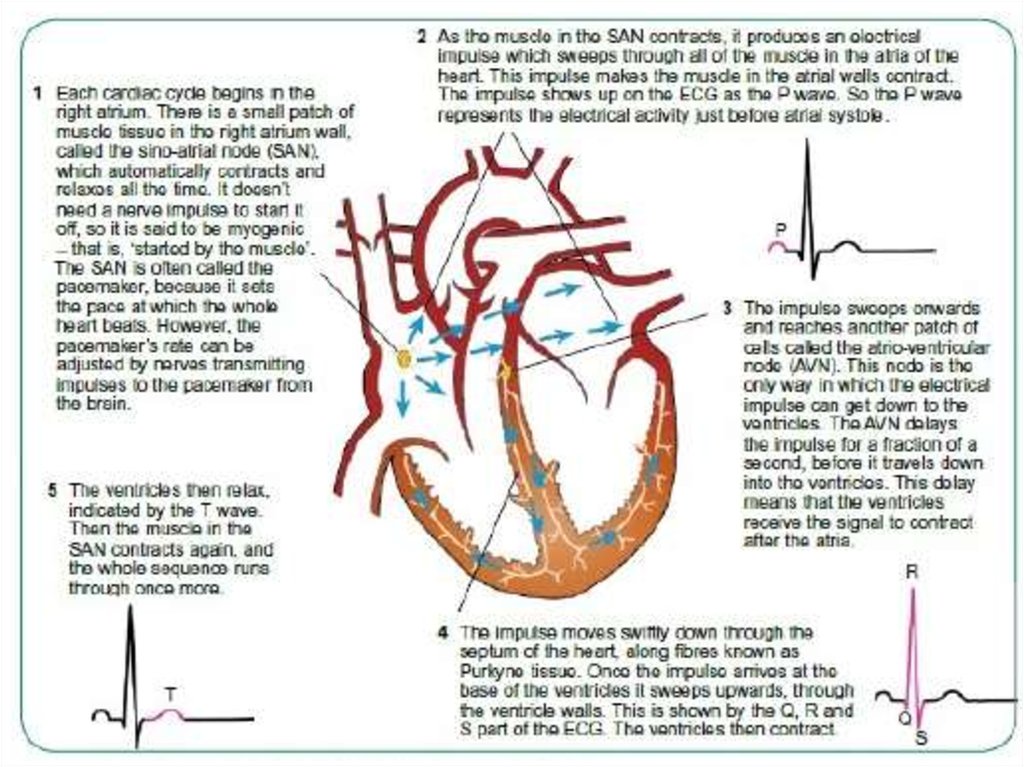



Electrical Processes Of The Heart Prezentaciya Onlajn
Conduction Pathway multiple rapid impulses from many atrial foci depolarize the atria in a totally disorganized manner at a rate of times a minute chaotic rhythm no clear P waves, no atrial contractions, loss of atrial kick, and an irregular ventricular response Pathophysiology/Effects decreases ventricular fillingThe heart has four chambers, two upper atria, the receiving chambers, and two lower ventricles, the discharging chambersThe atria open into the ventricles via the atrioventricular valves, present in the atrioventricular septumThis distinction is visible also on the surface of the heart as the coronary sulcus There is an earshaped structure in the upper right atrium called the right atrialStroke volume a volume of blood ejected by a ventricle during systole cardiac cycle sequence of events encompassing one complete contraction and relaxation of the ventricles and atria Term Name the elements of the intrinsic conduction system of the heart and describe the pathway of impulses through the system




Cell Accurate Optical Mapping Across The Entire Developing Heart Abstract Europe Pmc




What Part Of The Heart S Conduction System Acts As The Primary Pacemaker A Av Node B Bundle Of His C Purkinje Fibers D Sa Node Study Com
This delay allows time for the atria to empty their blood into the ventricles before ventricular contraction begins Atrioventricular Node, and Delay of Impulse Conduction from the Atria to the VentriclesThis study aims to understand the health and health needs of people in predominately black churches in Washington, DC This information will help researchers design programs to improve heart health in these communities To participate in this study, you must be between 19 and 85 years old and attend one of the churches in the studyAtria the two lower chambers of the heart are called Ventricles Each Valve is formed by two or three flaps called Leaflets The Valves that regulate the flow between the atria and the ventricles is called Atrioventricular Valves The Right AV valve, that prevents backflow from the right ventricle to the right atria is called Tricuspid Valve



As The Ventricles Contract The Valves Are All Chegg Com




The Cardiac Cycle Biology For Majors Ii
Kin 704 Atrial rhythm STUDY PLAY atrial dysrhythmias reflect abnormal electrical impulse formation and conduction in the atria, may occur because of altered automaticity or triggered activity (disorders in impulse formation);To gather information about impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles, study the P wave PR interval ST segment T wave PR interval (012) A nurse is caring for a client who has a HR of 42 and is symptomatic The nurse notifies the provider (PR interval Atria to Ventricle) (QRS less than 012)The conduction system is comprised of bundles of specialized large diameter muscle fibers located in the subendocardium throughout the ventricles These are called Purkinje Fibers Propagation of the impulse proceeds from the SA node through the atrium at about 01 to 1 m/sec and is greatly slowed while passing through the AV node to




Electrocardiographic Approach To Complex Arrhythmias Cardiac Electrophysiology Clinics




Decision Tree Predictive Learner Based Approach For False Alarm Detection In Icu Springerlink
Fig 2 A lateral epicardial view of the right atrium with the site of the SA node shown by the dashed pink line B and C endocardial views (normal and with transillumination) of the posterior and septal walls of the right atrium to show the oval fossa (OF) and limits of the triangle of Koch (dashed white lines), the tendon of Todazo (TT) and the insertion of the septal cusp of the




Aer 8 4 By Radcliffe Cardiology Issuu



Dadun Unav Edu Bitstream 1 Tesis Hawks19 Pdf



Lecture 13 Abn Conduction Pathology
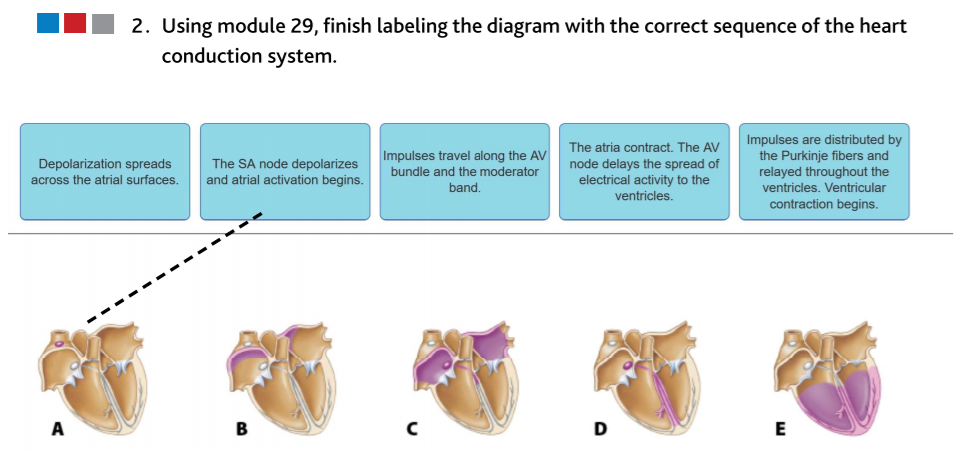



2 Using Module 29 Finish Labeling The Diagram With Chegg Com




Ecg Modules 1 2 Plus Lecture Flashcards Quizlet
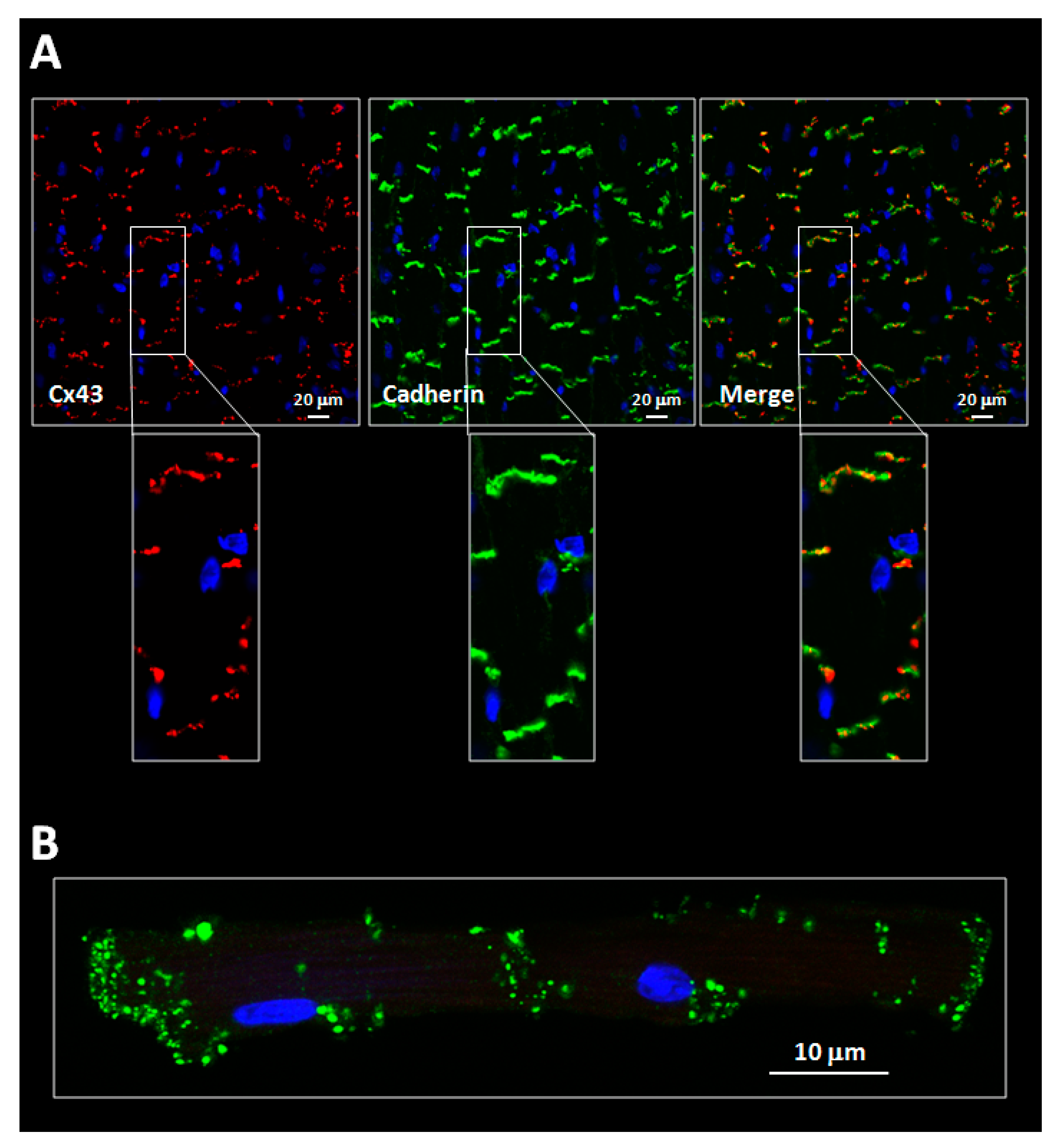



Ijms Free Full Text Connexins In The Heart Regulation Function And Involvement In Cardiac Disease Html




Comparison Of Metric And Cell To Cell Speed Measurements A Download Scientific Diagram




Relationship Between Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation And A Novel Electrocardiographic Parameter P Wave Peak Time Sciencedirect
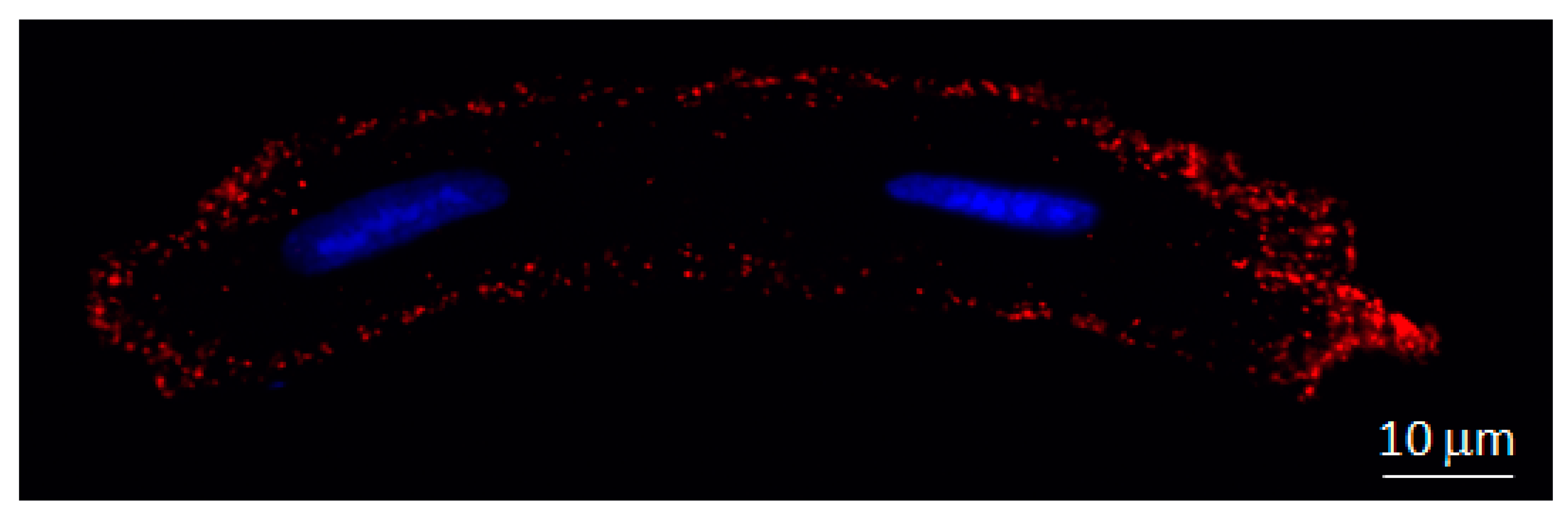



Ijms Free Full Text Connexins In The Heart Regulation Function And Involvement In Cardiac Disease Html




Ecg Interpretation Made Incredibly Easy Docsity




The Conducting System Of Heart



Repository Tudelft Nl Islandora Object Uuid 2a D762 40c4 21 Cf4cbffe0a6b Datastream Obj Download




Biology Xii Science Pages 151 0 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



Pdf Cardiac Conduction System Delineation Of Anatomic Landmarks With Multidetector Ct




The Basic Language Of Cardiac Electrophysiology An Introduction To Intracardiac Electrograms And Electrophysiology Studies Springerlink



1




Patient Education Syncope Fainting Beyond The Basics Uptodate



Fast Response Action Potential Of Contractile Cardiac Muscle Cell Ppt Download



Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Evaluation Of Ventricular Dysynchrony And Patient Selection Archivos De Cardiologia De Mexico



2



Modeling An Excitable Biosynthetic Tissue With Inherent Variability For Paired Computational Experimental Studies



Principles Of Emergency Medicine Section 1 An Introduction To Clinical Emergency Medicine




Aer 9 3 By Radcliffe Cardiology Issuu




Josephsons Clinical Cardiac Electrophysi
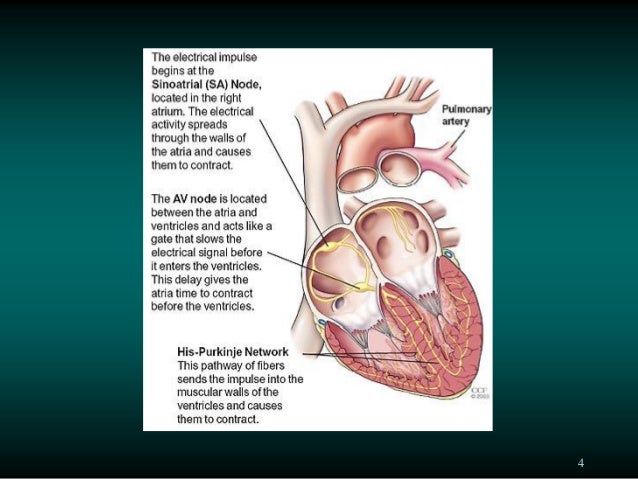



An Overview Of Paediatric Ecg




Electrocardiography Emg 1 Diagram Quizlet
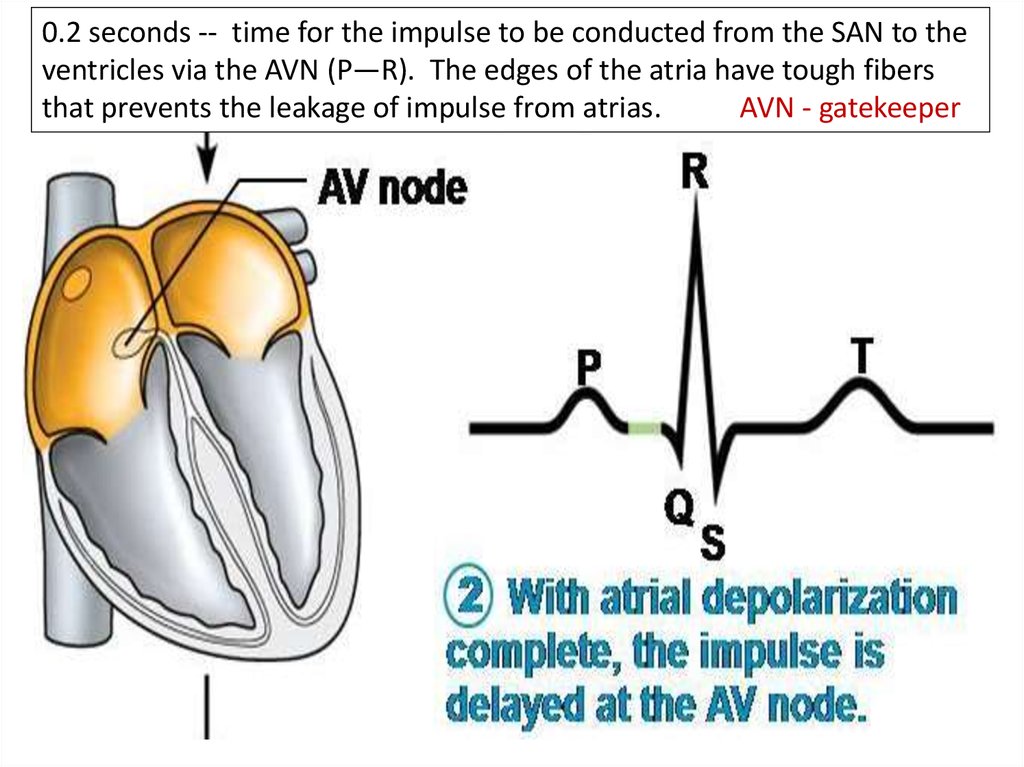



Electrical Processes Of The Heart Online Presentation




Interpreting A Rhythm Strip



Modeling An Excitable Biosynthetic Tissue With Inherent Variability For Paired Computational Experimental Studies




Relationship Between Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation And A Novel Electrocardiographic Parameter P Wave Peak Time Sciencedirect
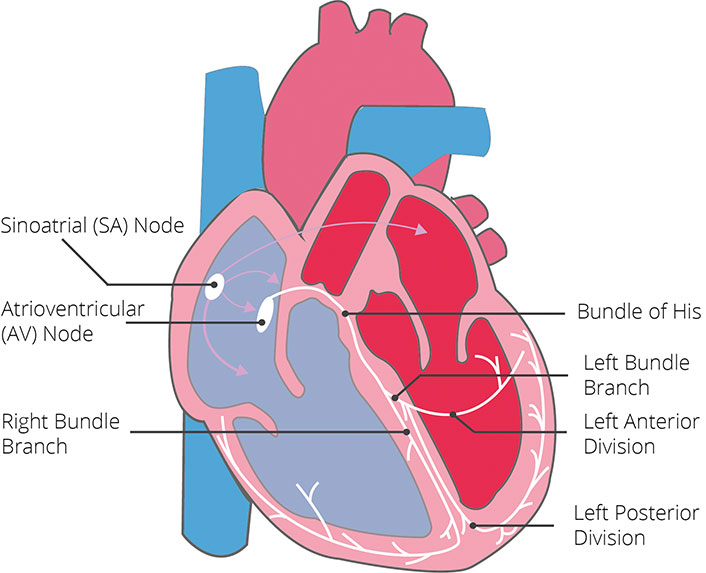



Electrocardiogram Ecg Cardiosecur
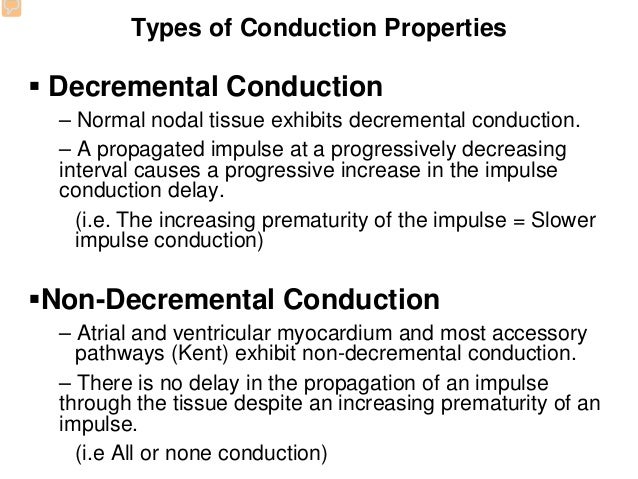



Electrophysiologic Study




Acute Atrial Dilatation Slows Conduction And Increases Af Vulnerability In The Human Atrium Ravelli 11 Journal Of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology Wiley Online Library




Pdf Mechanisms Of Arrhythmias And Conduction Disorders In Older Adults




Electrophysiology Study And Catheter Ablation
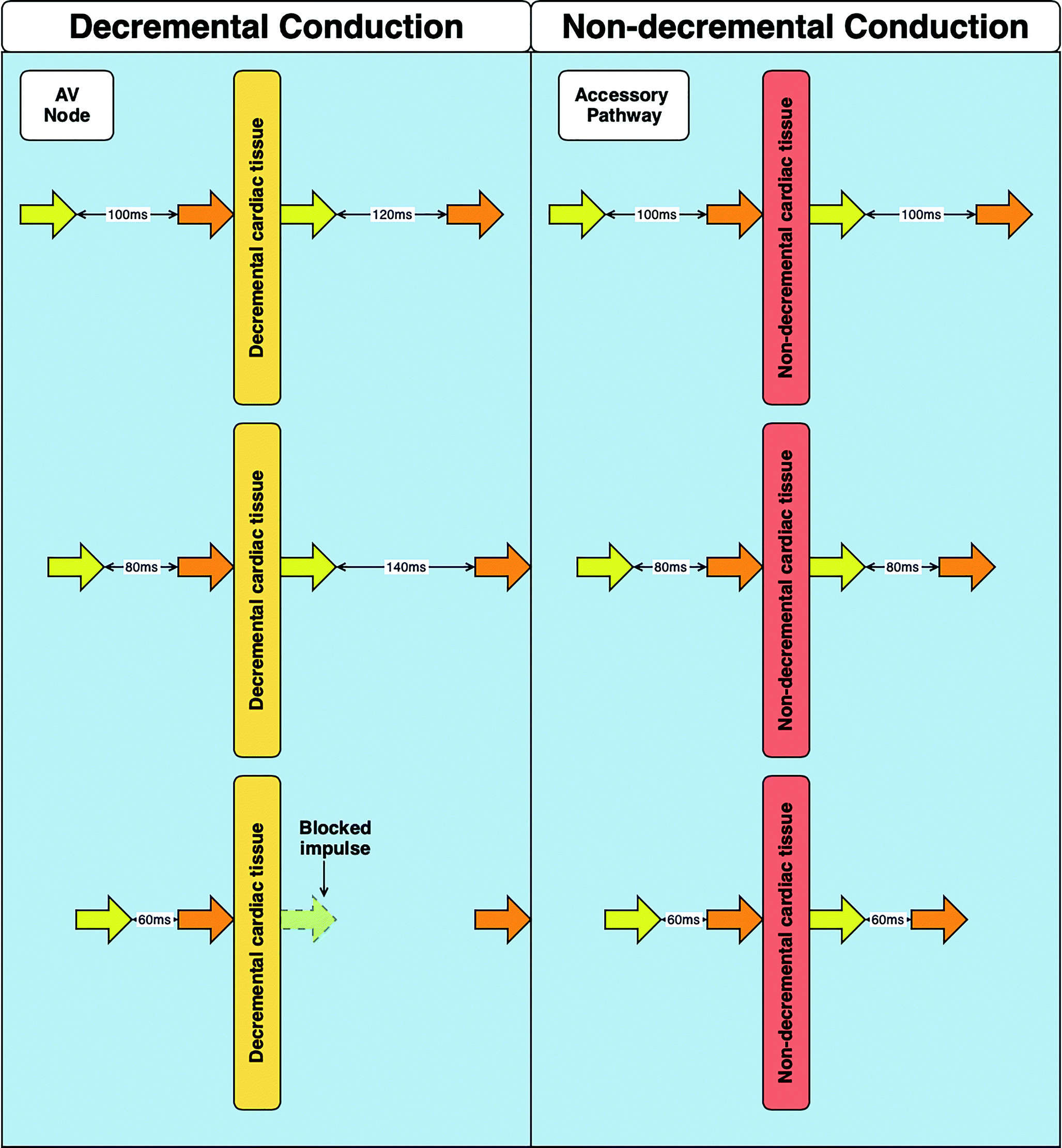



The Basic Language Of Cardiac Electrophysiology An Introduction To Intracardiac Electrograms And Electrophysiology Studies Springerlink
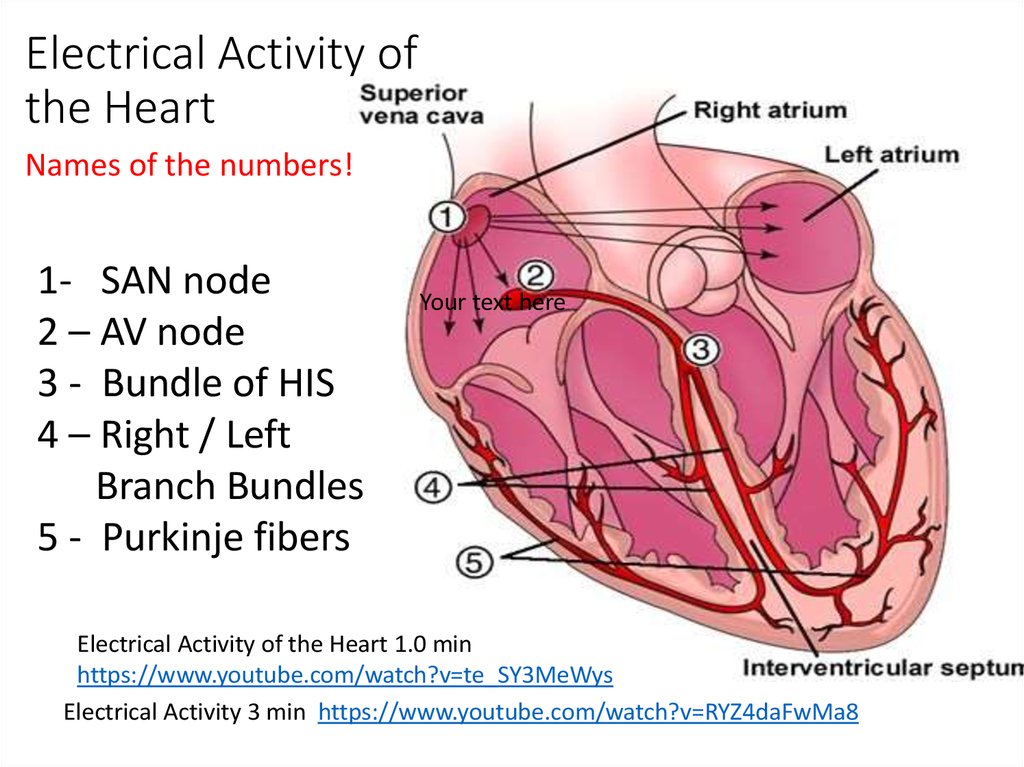



Electrical Processes Of The Heart Online Presentation




The Conducting System Of Heart
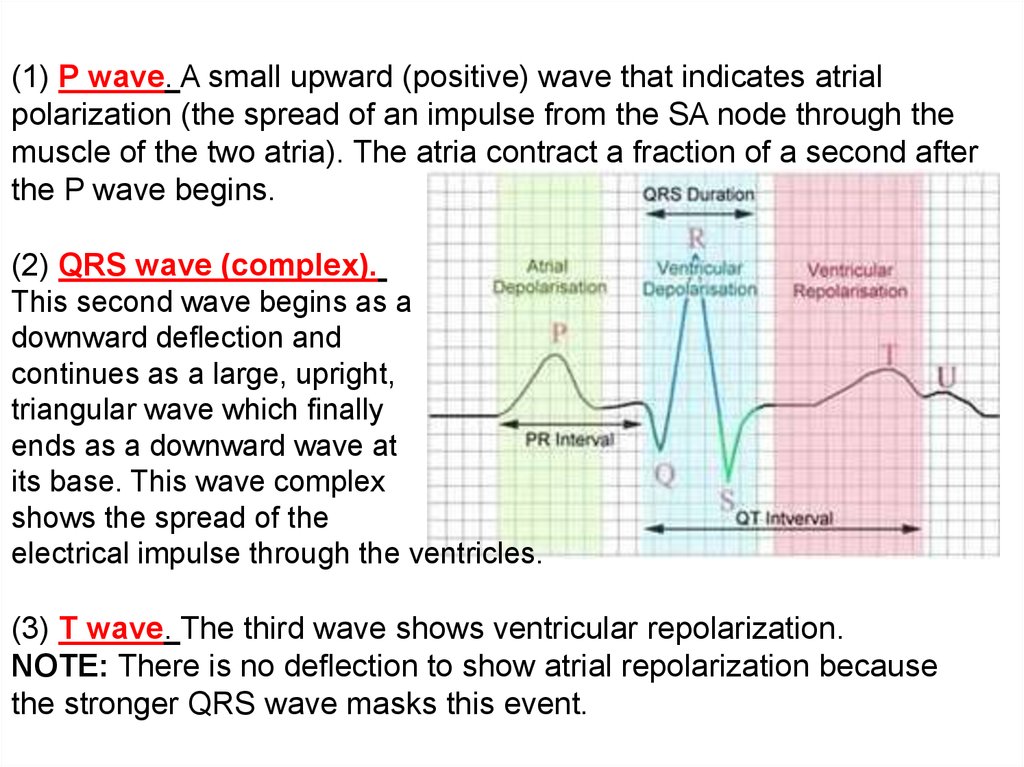



Electrical Processes Of The Heart Online Presentation




Electrophysiocardiogram International Journal Of Cardiology
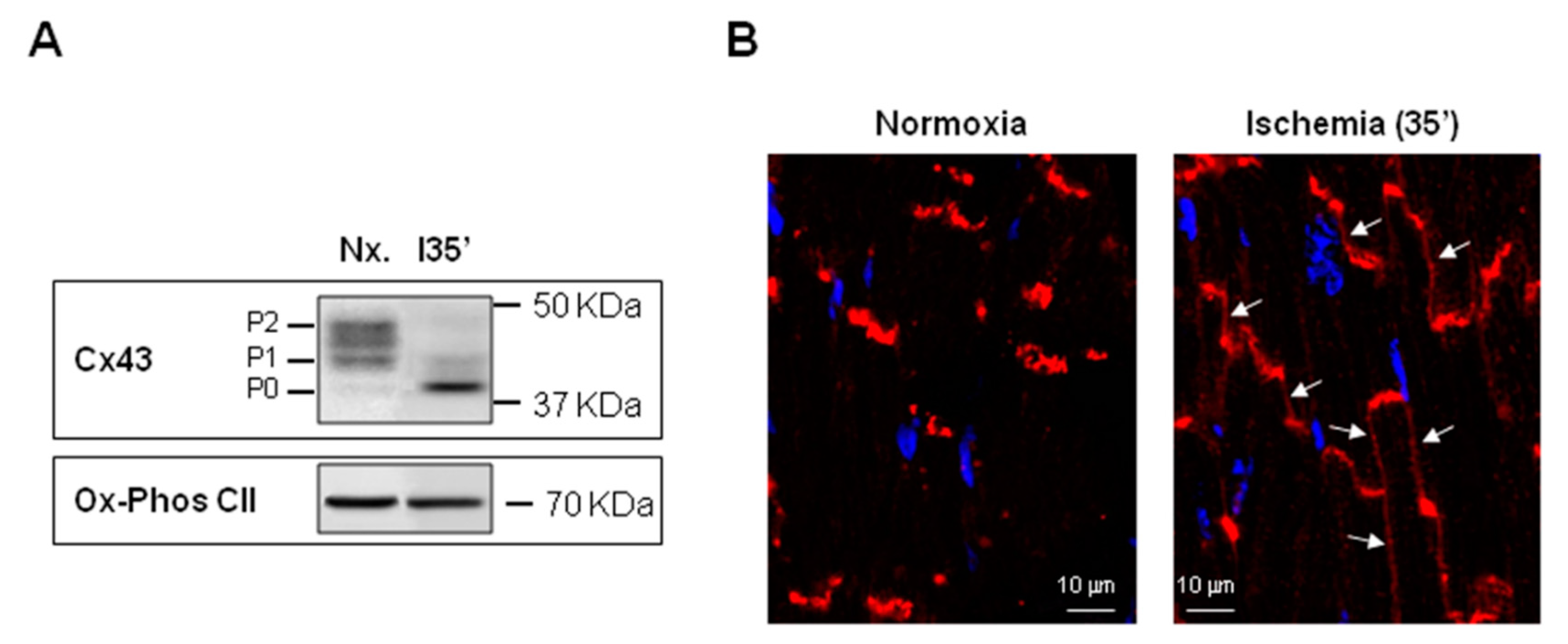



Ijms Free Full Text Connexins In The Heart Regulation Function And Involvement In Cardiac Disease Html




Electrophysiocardiogram International Journal Of Cardiology




Basic Ecg Interpretation 2 0 E Learning Notebook Pdf Pdf Heart Valve Heart




Basics Of Ecg



3



Electrophysiology Of The Heart Ppt Video Online Download



Www Ugent Be Di Laim En Research Horses Cardiology Pulmonaryveinspigsandhorses Pdf



Modeling An Excitable Biosynthetic Tissue With Inherent Variability For Paired Computational Experimental Studies




Cell Accurate Optical Mapping Across The Entire Developing Heart Abstract Europe Pmc




Congenital Atrial Standstill Associated With Coinheritance Of A Novel Scn5a Mutation And Connexin 40 Polymorphisms Heart Rhythm



Ecg Interpretation Made Incredibly Easy Docsity



1



Pacemaker And Icd Troubleshooting Intechopen




Anatomic Electrophysiological Correlations Concerning The Pathways For Atrioventricular Conduction Circulation




Electrical Processes Of The Heart Online Presentation




And The Beat Goes On The Cardiac Conduction System The Wiring System Of The Heart Boyett 09 Experimental Physiology Wiley Online Library



Approaches For Determining Cardiac Bidomain Conductivity Values Progress And Challenges Springerlink
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/iStock-616893490-59270be03df78cbe7eef363d.jpg)



When Is A Pacemaker Needed For Heart Block



1




Origin Of The Heartbeat The Electrical Activity Of The Heart Ganong S Review Of Medical Physiology 24th Edition



Frontiers Targeting The Substrate In Ablation Of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Recent Lessons And Future Directions Physiology
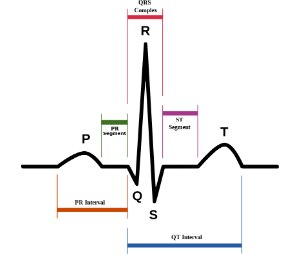



Ekg Rhythm Identification 10 Steps From Ems1 Com




Origin Of The Heartbeat The Electrical Activity Of The Heart Ganong S Review Of Medical Physiology 24th Edition



2




Pacemaker And Icd Troubleshooting Intechopen




And The Beat Goes On The Cardiac Conduction System The Wiring System Of The Heart Boyett 09 Experimental Physiology Wiley Online Library



Research Tue Nl Files 1014 Eerik Inen Pdf



Repub Eur Nl Pub 16 Dissertation Mihai Strachinaru Pdf




Print Product Index Ciplamed




The Human Task 4 Kcnk17 Mutation Gr C 262g A Contributes To The Download Scientific Diagram



2




Cell Accurate Optical Mapping Across The Entire Developing Heart Abstract Europe Pmc
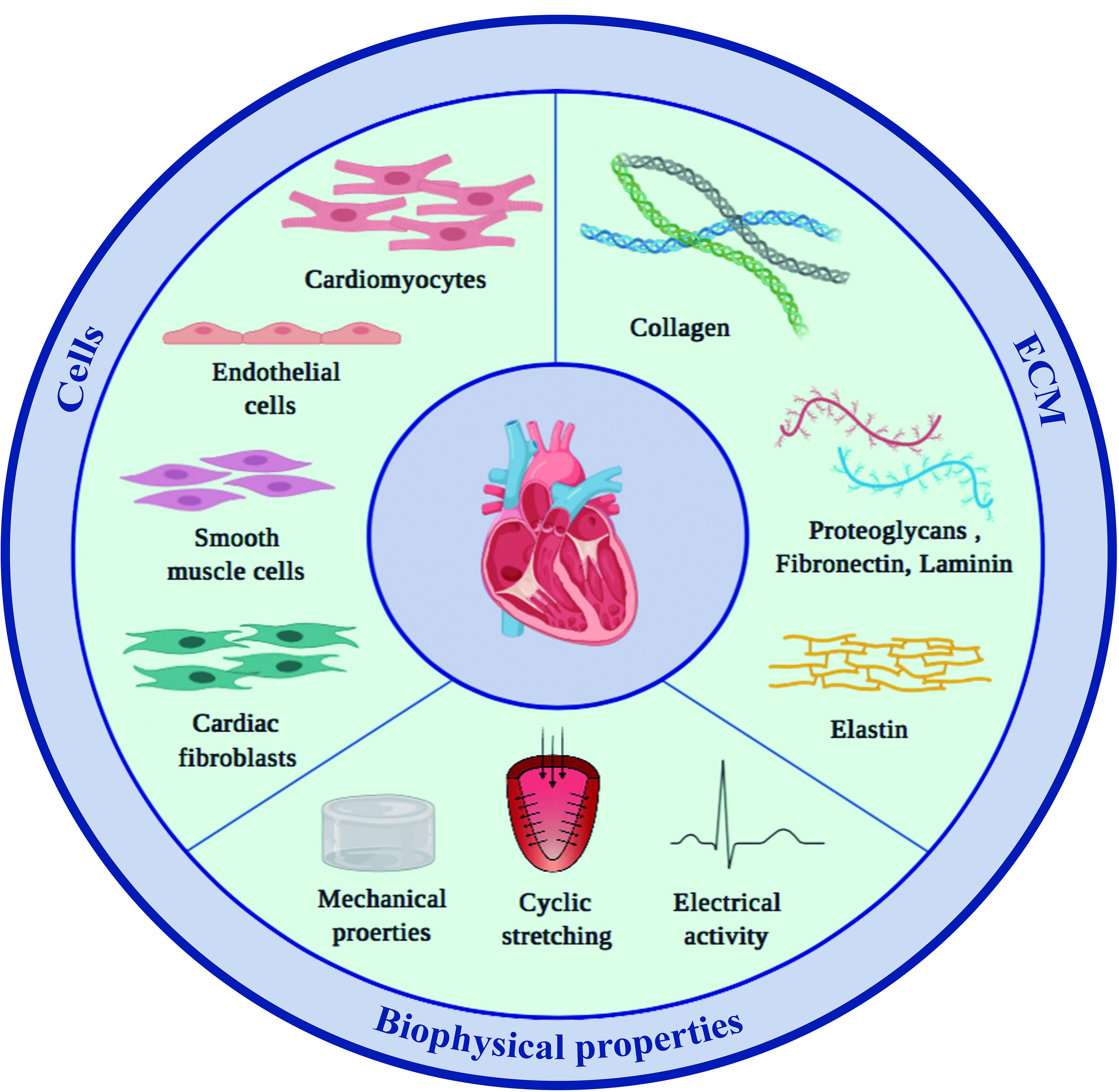



Frontiers Cells Materials And Fabrication Processes For Cardiac Tissue Engineering Bioengineering And Biotechnology




And The Beat Goes On The Cardiac Conduction System The Wiring System Of The Heart Boyett 09 Experimental Physiology Wiley Online Library




Cardiac Transmembrane Ion Channels And Action Potentials Cellular Physiology And Arrhythmogenic Behavior Physiological Reviews




Electrophysiocardiogram International Journal Of Cardiology



Modeling An Excitable Biosynthetic Tissue With Inherent Variability For Paired Computational Experimental Studies




Electrophysiocardiogram International Journal Of Cardiology



Repository Tudelft Nl Islandora Object Uuid 2a D762 40c4 21 Cf4cbffe0a6b Datastream Obj Download
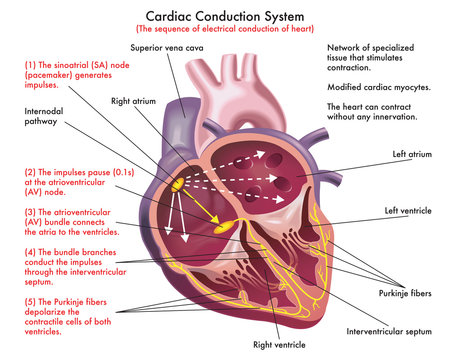



63 000 Best Conduction Images Stock Photos Vectors Adobe Stock



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿